Microsoft SQL Server Support FAQ
What is SQL Server CDM? How does it help solve my challenges?
Database administrators working extensively with SQL Server are challenged when faced with mission-critical use cases such as Backup, Recovery, DevOps, and Business Analytics. This is especially true given that their SQL Server databases have expanded in size and number over time, and that the databases need to be up and running 24x7x365.
SQL Server DBAs struggle with the following:
- Backups are slow, complex and need constant management
- Backup process slows down the production servers
- Recoveries are slow and complex
- Repurposing App consistent backups (clones) for DevOps and Business Analytics is slow, complex and storage inefficient
- Lack of automation exists for producing quick and secure clones required to accelerate DevOps
- Copy sprawl problems occur due to no central catalog of copies
- Unable to meet organization’s stringent RPO and RTO requirements
ECX simplifies SQL Server copy management by enabling administrators to orchestrate application-consistent copy creation, cloning and recovery in minutes, instead of hours or days. ECX copy management leverages the advanced snapshot and replication features of the underlying storage platform to rapidly create, replicate, clone, and restore copies of SQL Server databases in the most efficient way possible, in both time and space. ECX enables you to focus on the backup and restore requirements of your business rather than the technical details of the underlying storage platforms.
ECX is an intelligent copy data management solution that delivers end-to-end automation, orchestration, and self-service functionality for your SQL Server environment through a comprehensive and scalable catalog. With the self-service features of ECX, your users are empowered to create clones on demand, freeing DBAs, while at the same time offering the advanced recovery features needed for SQL Server environments.
ECX SQL Server Copy Data Management solution supports the following SQL Server deployment modes running on VMware virtual machines or physical servers:
- Standalone SQL Server – Databases running on a single server
- SQL Server Failover Cluster – SQL Server instances running on Windows Server Failover Clusters using Shared storage
- SQL Server Always On – Primary and secondary databases in Availability group configured across clusters of servers
ECX SQL Server CDM Solution Architecture
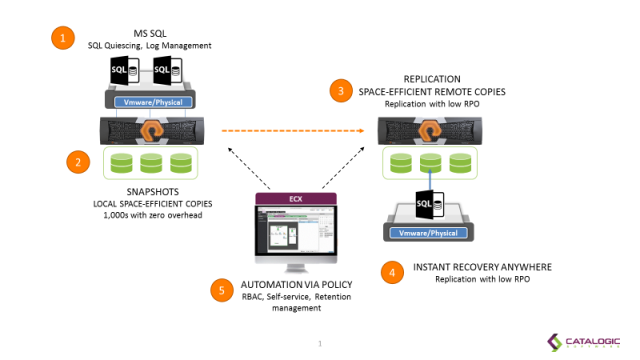
Deployment and Registration
Do I need to deploy any additional agents to protect SQL Server standalone, Failover Cluster or AlwaysON configuration?
ECX for SQL Server is delivered as a VMware OVA that is easily deployed on demand in a matter of minutes. Once deployed, you simply register your SQL Servers with appropriate credentials and then let ECX discover the rest. ECX eliminates the complexity of manually deploying and maintaining application agents on SQL Servers. A lightweight application-aware agent is automatically injected and updated to the required SQL Servers on demand.
SQL Server Backup workflow
Application-consistent SQL Server backup (local and remote) - Step by step
ECX auto-discovers databases and enables copies only of eligible databases. To be eligible for ECX backup, the SQL Server database needs to be residing on a supported storage platform. With ECX, application owners do not need to be concerned about storage infrastructure.
A typical SQL Server database backup creation workflow consists of following steps:
- Auto-inject lightweight agent into SQL Server node running database instance
- Discover storage volume mapping to selected SQL Server database(s) and logs
- Place SQL Server database in hot backup mode via VMware Snapshot/VSS Snapshot (App consistent)
- Automatically create consistency group for related storage volumes (only on physical servers)
- Create application-consistent backup (VADP backup and/or Storage snapshot)
- Take SQL Server database out of hot backup mode (Delete VM snapshot/VSS snapshot)
- Optionally create log copies with lowest RPO possible
- Catalog SQL Server database backups in catalog
- Optionally replicate application-consistent copy to remote location leveraging storage replication feature
ECX creates and uses in-place copies, so no data is physically moved. ECX generated application-consistent copies are both space and time efficient. With the same ease, a DBA can automate the creation of remote copies for disaster recovery use cases.
Does SQL Server solution leverage the storage consistency group feature?
The storage consistency group feature allows storage administrators to take a snapshot of database applications where the data is spread across multiple volumes to maintain consistency across all volumes.
In a typical SQL Server Database, the data is spread across different volumes for better IO performance and availability. On Physical servers, ECX SQL Server application-consistent copy creation ensures that appropriate consistency groups are automatically created to maintain consistency across all related volumes. ECX SQL Server backup on VM relies on VMware snapshots and doesn’t need to leverage storage consistency group feature.
What level of Application selection granularity is supported for SQL Server Backup jobs?
ECX SQL Server backup job definition supports copy selection at the following levels:
- One or more SQL Server Instances for Standalone SQL Server/Failover Cluster
- One or more Availability groups for AlwaysON
- One or more Databases for Standalone/Failover Cluster and SQL Server AlwaysON
Can I restore a database to an original instance and overwrite existing database in a single step?
Yes, use the Overwrite existing database option in the Application restore job definition.
Will ECX auto discover newly added SQL Server instances in a Standalone SQL Server and automatically protect it?
No. ECX will auto discover and present newly added SQL Server instances in the Backup job but you must explicitly select newly added SQL server instances for protection. Discovery of new SQL Server instances occurs as part of a regularly scheduled Application inventory job.
Will ECX auto discover newly added databases and automatically protect it?
Yes, if you select at Availability group level protection, ECX will auto discover newly added databases in selected availability group and protect it automatically during next job instance run. Discovery of new SQL Server instances and database occurs as part of regularly scheduled Application Inventory job.
Does ECX backup primary databases or secondary databases in SQL AlwaysOn?
ECX backs up only primary databases across the SQL AlwaysOn cluster.
Do SQL Server databases and logs need to be on supported storage for ECX CDM?
ECX also supports protection of SQL Server running on VMware VM configured on any storage that can be protected to supported storage systems via VM Replication. SQL Server running on physical servers require the database and logs to be on supported storage.
Does ECX perform full backups of databases?
ECX backups of SQL Server databases are always VSS COPY type backups.
SQL Server log management
Does ECX support Transaction log backup and log management?
Every SQL Server database has a transaction log that records all transactions and the database modifications made by each transaction. The transaction log must be truncated on a regular basis to keep it from filling up.
ECX provides you with an option to back up transaction log files. ECX supports log backup at a specified frequency. You can select one or more databases for log backup in a single backup job definition. Log destination can be specified as a single universal mount point or separate destination mount point for each database. Specified log backup destination path must already exist and must reside on supported storage system. If multiple databases are selected for backup, then each of the servers hosting the database must have their Destination directory set individually.
Does ECX support truncation of database logs?
Yes, ECX will automatically truncate log post log backups of databases that it backs up. If database logs are not backed up with ECX, its logs are not truncated by ECX and must be managed separately.
Can I specify a retention period for backed up transaction logs?
No. Log backup retention and auto-deletion is planned for a future release.
I am backing up transaction logs with ECX, but I don’t want it to truncate logs. Can I control this behavior?
No. This will be enhanced in future release of ECX.
Pre and Post Scripts
Does ECX support pre/post scripts for Application Database Backup jobs?
Yes, ECX supports job-level pre/post scripts and job-level pre/post Snapshot scripts to enable further customization.
Job-level prescripts and postscripts are scripts that can be run before or after a job runs.
Snapshot prescripts and postscripts are scripts that can be run before or after a storage-based snapshot subpolicy runs. (Please refer to pre/post script topic in the ECX User’s Guide for details.)
Data masking
Does ECX SQL Server solution offer Data Masking integration with third party masking tools?
A concern for security officers in any organization is that of keeping confidential information locked down, even internally. Data masking is used to hide confidential data, by replacing it with fictitious data, when making data copies for DevTest or other use cases. It prevents leakage of sensitive data in non-production databases via static data masking [SDM], and production data in transit via dynamic data masking [DDM].
The following Data Masking integration features will be available in a future release.
ECX will include integrated data masking workflows with the ability to leverage third party masking tools. Traditionally, data masking is difficult, slow, and storage-consuming, but with ECX it will be easily integrated into the SQL Server backup workflow, allowing creation of masked copies at a specified frequency. Masked copies are automatically marked in the catalog. Access to secure copies is managed by the administrator by leveraging the application-level RBAC.
In addition, SQL Server will enable you to leverage the Dynamic Data Masking feature of SQL Server 2016.
Is sample masking script provided with ECX SQL Server solution?
A sample data masking script can be provided upon request. A sample masking script demonstrates data masking integration with built-in Dynamic Data masking script of SQL Server 2016. This feature will be available in a future release.
SQL Server Restore Workflow
Can I leverage SQL Server database clones for multiple use?
Limitations of current tools and approaches:
- Database cloning requires action by DBAs and is gated by process
- QA relies on DBAs for cloning the databases for functional testing
- The database cloning is gated by processes (space requisition, approvals, etc.)
- Database cloning is not time- or storage-efficient
- Usage of common cloning tools or custom scripts creates full copy requiring large amounts of additional storage
- Creating full copies is slow
ECX solves these challenges with simple, automated end-to-end clone lifecycle management:
- Self-service access to secure clones by QA team eliminates administrative and process bottlenecks
- ECX enables rapid database clones that are both time- and space-efficient
- Provision clones in minutes regardless of its size
- Leverages underlying storage snapshots for space efficiency
- ECX promotes standardization and governance through centralized catalog, granular RBAC, and automated policies
Your SQL Server clones can be utilized and consumed instantly – for whatever your use case -- through ECX “Instant Disk Restore” jobs. ECX catalogs and tracks all cloned instances. Instant Disk Restore can leverage iSCSI or FC protocol to provide immediate mount of LUNs without transferring data.
Can I create an Instant Clone of a SQL Server database for DevOps and Business Analytics?
ECX provides automated workflows to create instant clones of SQL Server database regardless of its size.
- Instantly create database clones from any of the copies in the ECX inventory, at local or remote locations, to accelerate Business Analytics.
- Enable and accelerate DevOps by providing Instant Disk Restore to secure clones of databases to appropriate users via application-level RBAC.
Then, when your TestDev, DevOps, or research/analytics work is completed, you can save the clone to more permanent storage or simply tear it down.
What is the granularity of database recovery supported by ECX?
Supported recoveries for standalone or AlwaysOn:
- Database can be recovered to point of snapshots to original or new instance (Instant Disk Restore)
- Database can be recovered to point in time leveraging backed up transaction logs (Instant recovery) to original or new instance
- Database can be recovered using new name to original or new instance
- You can select one or more databases in a single restore job definition.
- Each selected database in a Restore job definition can have separate destination specification
- Databases are always recovered in online mode
- Database can be recovered from standalone instance to AlwaysON Availability group
- Database from AlwaysON Availability can be recovered to standalone instance
- Database running on older version can be recovered to instance running same or newer version.
What granularity of Point in Time recovery is supported?
ECX enables database recovery to a specific point in time, allowing you to:
- Restore to the state just before the point of failure
- Restore multiple databases to a consistent time
Can I restore a Database to a Transaction Mark?
No. This will be enhanced in a future release of the product.
Does ECX support recovery of system databases?
System database (master, msdb, model) recovery is presently not supported from application restore workflows. You can leverage VM restore workflows to fulfill a recovery use case requiring a system database recover.
Does ECX support recovering a database in online mode?
Yes, Instant Disk Restore or Instant Database Restore recovers databases in online mode.
Does ECX support recovering databases in an offline state (norecovery)?
No. This will be enhanced in a future release of the product.
Does ECX support recovering databases in a standby/read-only state (standby)?
Yes, ECX provides an application option to control this behavior.
Roll back uncommitted transactions and leave the database ready to use
- Select this option to restore the database to an online state. If selected, additional transaction logs cannot be restored. If deselected, uncommitted transactions are not rolled back, leaving the database non-operational. Additional transaction logs can then be restored.
Does ECX support recovering database with Restricted Access?s
No. This will be enhanced in a future release of the product.
Does ECX support restoring only logs so that they can be applied to a standby database?
No, not from the ECX application restore workflow. A user can easily access the transaction log backup location from the SQL server and perform this outside of the product.
Does ECX support out-of-place restore?
Out-of-place restore is used to relocate a database file to a new location:
- Copying/moving a database to a different location on a same SQL Server instance
- Copying a Database to a different SQL Server Instance at a different location
This feature will be enhanced in a future release of the product.
Where are SQL specific and ECX specific logs if errors occur?
All required logs (ECX and application) are collected as part of the current log collection functionality. There should be no need to manually obtain SQL application logs from within SQL Server VMs.
How do I refresh? How to promote to Production?
All database recovery operations can leverage Instant mode (Test) and then can either be deleted or promoted to permanent mode via workflow control. This behavior can be controlled via the Make Permanent job option.
- Enabled - Always make permanent
- Disabled - Never make permanent
- User election - Allows the user to select Make Permanent or Cleanup when the job session is pending
Does ECX use existing hardware providers for physical SQL backups?
No. ECX automatically deploys its own VSS HW provider service for SQL Server running on physical servers. It is automatically started on demand during SQL Server Backup jobs. At the completion of the backup job, the VSS HW provider service is automatically stopped.
When ECX protects a SQL VM with pRDM, can it restore a database back to the original node as a pRDM?
Currently, a SQL VM with pRDM must be registered as Physical in ECX. Hence, the restoration of that data obeys the Physical restore restrictions, which means it can only restore back to the original host via iSCSI. If the target host being restored to was registered as Virtual, then the database would be restored as a pRDM.
This functionality will be improved in future release.
Why must I choose a proxy node when performing a restore to a SQL Failover cluster?
Windows requires signatures to be unique, so when you attach a disk that has a signature equal to one that is already attached, Windows keeps the disk in “offline” mode and doesn’t read its partition table or mount its volumes. To prevent disk signature collision, during Instant Database Restore, ECX leverages Windows proxy servers to temporarily mount disks from snapshots, generate a new signature, then mount to original server.
Any Windows node with iSCSI or Fibre Channel access to the storage can be selected as a proxy server, provided that the node is not part of the original cluster. It is recommended to select a standalone virtual or physical Windows node as a proxy server.
Self Service
Does ECX support RBAC? What is the level of granularity supported for SQL Servers?
Role-based access control allows you to set the resources and permissions available to ECX accounts. Through role-based access control you can tailor ECX for individual users, giving them access to the features and providers they need.
Using ECX RBAC functionality, user can delegate ECX role to enable and accelerate DevOps by providing Instant Access to secure clones of databases to appropriate users via application-level RBAC. Then, when your TestDev, DevOps, or research/analytics work is completed, you can save the clone to more permanent storage or simply tear it down.
Can developers access ECX operations using command line or APIs?
A rich set of REST APIs are provided to enable full access to ECX functionalities for further customization. Please refer to Product Marketplace for full API documentation and a facility that allows to you to experiment with ECX APIs.
System Requirements
What SQL Server versions are supported and on what Windows OS? What are supported Storage Systems for Microsoft SQL Server?
The Microsoft Server SQL Support Matrix is below.
| Database Versions/Types and Operating Systems | Server Types | Storage Systems | Storage Configuration |
Standalone, SQL Server Failover Clustering, and AlwaysOn configurations are supported for SQL 2008 R2 SP4, SQL 2012, SQL 2014, and SQL 2016.[2] Note: It is highly recommended to install the latest SQL Server patches and updates in your environment. |
Physical [7] [8] [9] [10] |
|
|
| Virtual
(VMware) [3] |
Note: VM Replication restore jobs can be run to store off-host copies on the storage systems listed above. |
|
[1] Windows Remote Shell (WinRM) must be enabled. By default, WinRM is not enabled in a Windows Server 2008 R2 environment. To ensure services in a Windows Server 2008 R2 environment are able to receive connections, perform the following procedure: Run winrm quickconfig, then select Yes to make changes. This adds a listener for port 5985. To ensure the listener is available, enter the following command: winrm e winrm/config/listener.
[2] Note that Clustered Shared Volumes (CSV) are not supported.
[3] See System Requirements for supported VMware vSphere versions.
[4] Select the Physical provider type when registering the provider in ECX. Recoveries require direct access to storage. Note that NetApp ONTAP and DellEMC storage systems are not supported.
[5] vRDMs are supported through VM Replication jobs.
[6] Independent disks are supported only if the underlying storage utilizes supported storage systems. Register the SQL resource as Physical when configuring the provider in ECX. Note that independent disks do not allow snapshots to be taken in VMware virtual scenarios. The above listed IBM Spectrum Accelerate, IBM Spectrum Virtualize, and Pure Storage FlashArrays are supported for physical registration.
[7] When registering physical SQL servers it is recommended to register via the DNS server. The ECX appliance must be resolvable and route-able by the DNS server; the physical SQL server will communicate back to ECX through DNS.
[8] Recovery for target servers registered as Physical provider types requires direct access to storage.
[9] Any Windows node with iSCSI or Fibre Channel access to the storage can be selected as a proxy server, provided that the node is not part of the original cluster. It is recommended to select a standalone virtual or physical Windows node as a proxy server.
[10] Note that for physical SQL servers, you must allow outgoing connections to port 8443 on the ECX appliance from the SQL server.
SQL servers residing on any storage can also be protected to supported storage systems through VM Replication jobs.
For both physical and virtual SQL environments, point-in-time recoveries beyond the last snapshot taken are incompatible with workflows utilizing more than one Site. In a virtual environment, the SQL server, associated vCenter, and storage must be registered to the same site. In a physical environment, the SQL server and storage must be registered to the same site.
What are Environment and permission requirements for SQL Server solution?
Note the following Microsoft environmental requirements:
- Windows Remote Shell (WinRM) must be enabled
- The SQL user must enable the public and sysadmin SQL permissions.
- The user identity must have sufficient rights to install and start the ECX Tools Service on the virtual machine node. This includes "Log on as a service" rights. For more information about the "Log on as a service" right, see https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794944.aspx.
- The fully qualified domain name must be resolvable and route-able from the ECX appliance
- The virtual machine node DNS name must be resolvable and route-able from the ECX appliance
- The VMGuest version must be current
- VMware Tools must be installed on the virtual machine node
Does ECX support SQL Server 2016 running on Windows 2016?
Yes. See the matrix above.
Does ECX support SQL Server configured as Physical RDMs, or Independent disks?
Yes. See footnotes 4 and 6 in the matrix above.
Does ECX support SQL Server configured as Virtual RDMs?
Yes. For limitations see footnote 5 in the matrix above.
Does ECX support SQL Server running on physical machine(s)?
Yes. See the matrix above.
Are there additional requirements for SQL support in ECX?
SQL Support for VMware Virtual Machines
UUID must be enabled to perform Microsoft SQL-based backup functions. To enable, power off the guest machine through the vSphere client, then select the guest and click Edit Settings. Select Options, then General under the Advanced section. Select Configuration Parameters..., then find the disk.EnableUUID parameter. If set to FALSE, change the value to TRUE. If the parameter is not available, add it by clicking Add Row, set the value to TRUE, then power on the guest.
The virtual machine must use SCSI disks only, dynamic disks are not supported.
The latest VMware Tools must be installed on the virtual machine node.
In-Memory OLTP Requirements and Limitations
In-Memory OLTP is a memory-optimized database engine used to improve database application performance, supported in SQL 2014 and 2016. Note the following ECX requirements and limitations for In-Memory OLTP usage:
- The maximum restore file path must be less than 256 characters, which is a SQL requirement. If the original path exceeds this length, consider using a customized restore file path to reduce the length.
- The metadata that can be restored is subject to VSS and SQL restore capabilities.
SQL Server Failover Clustering Requirements for Windows Server 2008 R2
The Failover Cluster Manager Snap-In must be imported and configured before running ECX Backup and Restore jobs. To import, run Windows PowerShell in Windows Server 2008 R2 and enter the following command: import-module failoverclusters
For more information, see https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee461009.aspx.
Registration and Authentication
Register each SQL server as a provider in ECX by name or IP address. When registering a SQL Cluster (AlwaysOn), register each node by name or IP address. The fully qualified domain name and virtual machine node DNS name must be resolvable and route-able from the ECX appliance.
The user identity must have sufficient rights to install and start the ECX Tools Service on the node. This includes "Log on as a service" rights. For more information about the "Log on as a service" right, see https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794944.aspx.
The default security policy uses the Windows NTLM protocol, and the user identity format follows the default domain\Name format.
Kerberos Requirements
Kerberos-based authentication can be enabled through a configuration file on the ECX appliance. This will override the default Windows NTLM protocol.
For Kerberos-based authentication only, the user identity must be specified in the username@FQDN format. The username must be able to authenticate using the registered password to obtain a ticket-granting ticket (TGT) from the key distribution center (KDC) on the domain specified by the fully qualified domain name.
Kerberos authentication also requires that the clock skew between the Domain Controller and the ECX appliance is less than 5 minutes. Note that the default Windows NTLM protocol is not time dependent.
Privileges
On the SQL server, the system login credential must have public and sysadmin permissions enabled, plus permission to access cluster resources in a SQL AlwaysOn environment. If one user account is used for all SQL functions, a Windows login must be enabled for the SQL server, with public and sysadmin permissions enabled.
Every SQL instance can use a specific user account to access the resources of that particular SQL instance.
Catalogic ECX™ 2.6
© 2017 Catalogic Software, Inc. | All rights reserved.
MySupport | Knowledge Base | Trademarks | info@catalogicsoftware.com